| Lesson 2 | How data is stored |
| Objective | Identify table structures used in relational databases. |
Table Structures Relational Databases
A database is a collection of information that is usually related.
For example, a customer database might contain the customer's name, address, phone number, and account number.
Each data set for a customer is called a customer record, and each piece of information in the data set is a data element, or field.
A field is where one item of information is stored as a record. For example, an employee database might have one record per employee.
The individual pieces of information such as last name, first name, and social security number are known as fields.
In database terminology, a database is an organized collection of data, typically stored and accessed electronically from a computer system. Each record in this database represents a single, distinct entry, such as a customer or an employee, containing all the related data for that entity. Each record is composed of several fields or data elements, which are individual units of data. In your example of an employee database, fields like "last name," "first name," and "social security number" are specific data elements that make up one employee's record. This structure allows for efficient data management, retrieval, and manipulation, as each piece of information is neatly categorized and can be accessed or modified independently from the others within the same record. However, please note that in practice, it's crucial to handle sensitive data like social security numbers with strict privacy and security measures due to their confidential nature. Hence, a database contains tables, tables contain rows, and records contain columns.
In database terminology, a database is an organized collection of data, typically stored and accessed electronically from a computer system. Each record in this database represents a single, distinct entry, such as a customer or an employee, containing all the related data for that entity. Each record is composed of several fields or data elements, which are individual units of data. In your example of an employee database, fields like "last name," "first name," and "social security number" are specific data elements that make up one employee's record. This structure allows for efficient data management, retrieval, and manipulation, as each piece of information is neatly categorized and can be accessed or modified independently from the others within the same record. However, please note that in practice, it's crucial to handle sensitive data like social security numbers with strict privacy and security measures due to their confidential nature. Hence, a database contains tables, tables contain rows, and records contain columns.
Database Table Defined
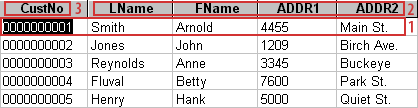
CustNo LName FName ADDR1 ADDR2 1 Smith Arnold 4455 Main St. 2 Jones John 1209 Birch Ave. 3 Reynolds Anne 3345 Buckeye 4 Fluval Betty 7600 Park St. 5 Henry Hank 5000 Quiet St.CustNo, LName, FName, ADDR1, ADDR2
- This image shows a portion of a customer database. Each row in the table represents a single record, which contains specific information for each customer.
- Each table column contains a specific record field. Every piece of information for each customer is stored in the individual fields. The information contained in this database includes the customer number [CustNo], last name [LName], first name [FName], address [ADDR1], and more, which is not visible in this image.
- The Customer Number is used to uniquely identify each record and is called a "unique key."
This example of a customer table contains one record per customer. The CustomerNo uniquely identifies each customer. Most databases consist of more than one table, and a common field such as the customer number, ties the tables together and produces a relationship between them. For example, in the course project, VirtualBookShelf, the database contains three tables:
- customers,
- books, and
- sales.
This is a simple database, but the idea is that the customer and book tables contain different information for different purposes. The sales table will contain information from these two tables when a purchase is made. When a purchase is made, information from these two tables, such as customer number and item number are written to the sales table. This forms a relational database [2]. In the real world, though, the customer and inventory databases would probably be separate. The following graphic shows a sales transaction table that has a customer number column, which also matches the customer number column in the customer table.
ASP.NET in Action

SaleTable
| CustNo | ItemNo | Qty | Date | |-------------|--------|-----|------| | 0000000003 | (empty) | 0 | (empty) |
CustTable
| CustNo | LName | FName | ADDR1 | |-------------|-----------|-------|------| | 0000000003 | Reynolds | Anne | 3345 |
Observations
- SaleTable contains a record with
CustNo = 0000000003, but theItemNoandDatefields are empty, and theQtyis0. - CustTable contains a record with
CustNo = 0000000003, corresponding to a customer named Anne Reynolds with an address value of3345.
The field Customer Number forms a relationship between the tables. CustNo 00001 in the sales table represents the same customer in the customer table. Such relationships can exist among several tables in a database. The sales table can contain more than one entry per customer for each purchase a customer makes. Using a structure such as this, an application can iterate[1] through the customer table and prepare a sales report for each customer. In the next lesson, common database systems will be discussed.
[1]iterate: To execute program statements zero or more times in a loop structure.
[2]Relational database: This is a database that is organized and accessed based on relationships between tables, rows, and columns.