| Lesson 3 | Backup set syntax |
| Objective | Identify the syntax of the backup command. |
Oracle Backup set syntax
Backup sets are created with thebackup command in Recovery Manager.
Though you were briefly introduced to this command in the previous module, there are many syntax options for this powerful command.
The backup command
Earlier in this course, you were introduced to the basics of the
backup command-the backup type, tag, and
backup_spec portions of the command. Additional options can be used with the command, two of which are explained below.
formatspec
The formatspec tag can be used as part of the
The
backup command, which means it will apply to all backup specs in the command or to an individual backup_spec. The tag can also be used in the allocate command to apply to all files that will use that channel.The
formatspec tag consists of the keyword format, followed by a format spec in single quotes. The format spec includes literal characters and specific substitution variables that are automatically replaced by RMAN. For instance, the %d substitution variable is automatically replaced with the name of the database, the %t substitution variable is automatically replaced with the
timestamp, and so on.
SKIP
TheSKIP keyword can be used for the entire backup or for a specific backup set. The SKIP keyword is followed by one of three choices:
OFFLINE,which will skip any offline data filesREADONLY,which will skip any data files that are read-onlyINACCESSIBLE,which will skip any data files or archived redo logs that cannot read due to I/O errors.


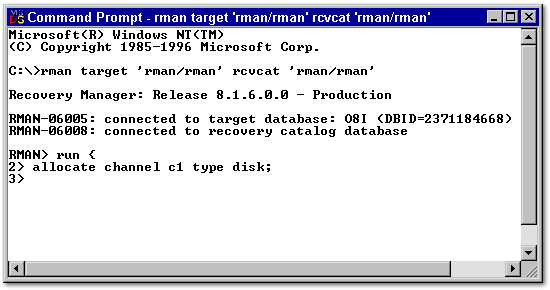



- Begin the backup process with the run command and press Enter.
- Prompt
- run
- Type run and press enter.
- Allocate a disk channel called ch1 and press Enter.
- Prompt
- allocate channel c1 type disk
- Type allocate channel c1 type disk; and press enter.
In the next lesson, you will learn how RMAN combines blocks from different files in a single backup piece, and about another important option for the
backup command.